Zi5sGS <a href="http://hdhpmrnrkrqd.com/">hdhpmrnrkrqd</a>, [url=http://sklrqssdmote.com/]sklrqssdmote[/url], [link=http://fzwegricddwf.com/]fzwegricddwf[/link], http://uyedsqnmmwhl.com/
SZ8vEx <a href="http://idmoaseuwnnn.com/">idmoaseuwnnn</a>, [url=http://lesgjjimdhth.com/]lesgjjimdhth[/url], [link=http://iaunixbrmrwi.com/]iaunixbrmrwi[/link], http://wgxgrjappnwr.com/
Domain Analysis
Strategic Dependency Model and Context Diagram
In the following figure the strategic dependency diagram for the e-Government case study
is reported. The diagram reports the dependency between User (a Citizen, a Government Agency or a
Company) and Public Body to the satisfaction of the goal Require service; moreover User depends on
the Certifier service to gain trust on the obtained output, while the Certifier service is needed by the
Public Body to authenticate the service output. Moreover User needs the E-payment service to satisfy
the softgoal Charge Fee.

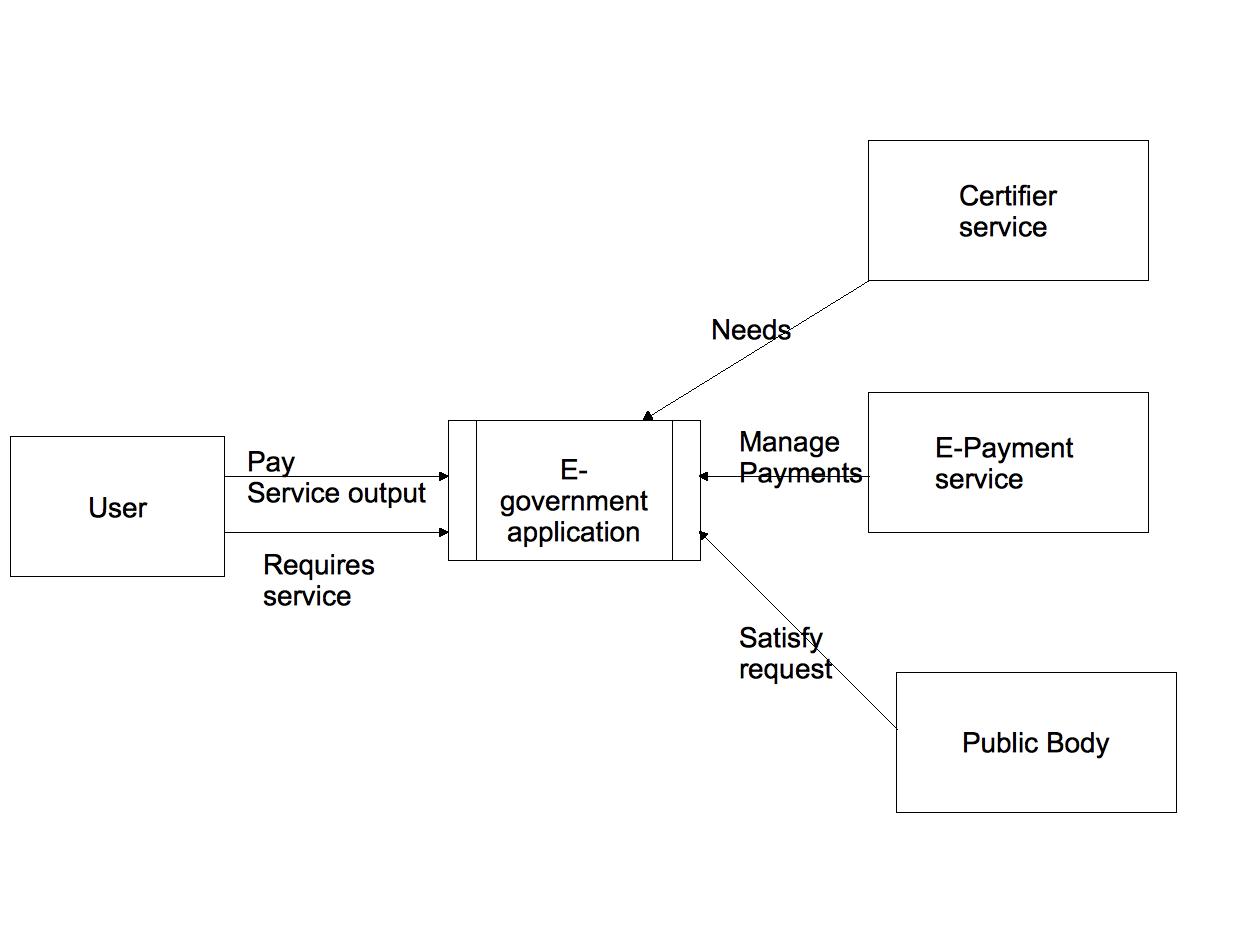
The following figure represent the context diagram of the e-government case study.
In the next figure the domain model of the e-Government is reported.
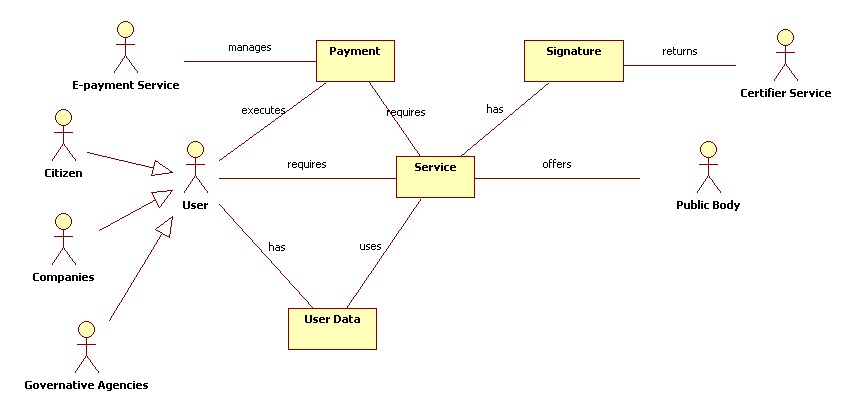
Domain Model
Scenarios
In the following figure the general use case diagram for the e-Government case study is reported.
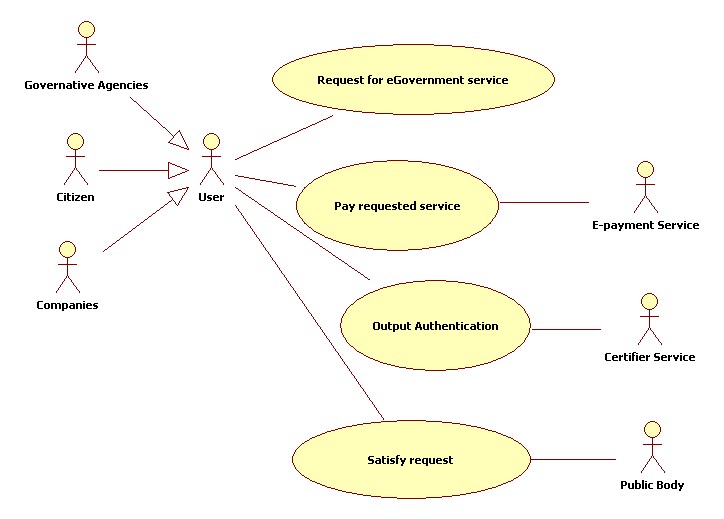
Table S1: Scenario TIS-ENG-1
| Field |
Description
|
| UniqueID
|
TIS-ENG-1
|
| Short Name
|
Request for e-Government service
|
| Related To
|
TIS-BG-1, TIS-BG-3, TIS-BG-4, TIS-BG-5, TIS-BG-6
|
| Involved Actors
|
User
|
| Detailed Operational Description
|
This scenario describes the submission of applications to obtain subsidies from the province of Bolzano, Italy. In the e-government application the process is started by the user that, after the login, chooses the service he needs. So the user inserts the needed data to compile the form for the request (he could decide to compile the form from the scratch or updating preexistent data). Actors involved in the scenario are the users of the application (citizen, companies or government agencies).
|
| Problems and Challenges
|
When a user requires a document or a service he submits a lot of personal data. The confidentiality of the data must be guaranteed by the application, moreover the user must be assured that provided data are not used outside that transaction.
|
| Additional Material
|
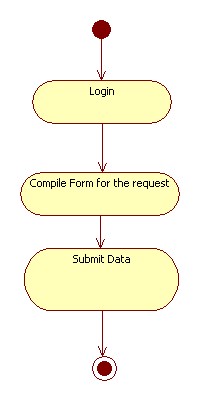
|
Table S2: Scenario TIS-ENG-2
| Field |
Description
|
| UniqueID
|
TIS-ENG-2
|
| Short Name
|
Pay requested service
|
| Related To
|
TIS-BG-5, TIS-BG-6
|
| Involved Actors
|
User, E-payment servi
|
| Detailed Operational Description
|
If the user needs to pay some fee to obtain the requested service, he must interact with the e-payment service. The user inserts the needed data (usually credit card number) and waits for the completion of the process. The e-payment service checks the inserted data for the payment.
|
| Problems and Challenges
|
A mechanism of encryption of data must be guaranteed to protect the transmission of confidential data by intrusion.
|
| Additional Material
|

|
Table S3: Scenario TIS-ENG-3
| Field |
Description
|
| UniqueID
|
TIS-ENG-3
|
| Short Name
|
Output Authentication
|
| Related To
|
TIS-BG-5, TIS-BG-6
|
| Involved Actors
|
User, E-Certifier service
|
| Detailed Operational Description
|
The user could require an authenticated output, so the application has to provide a mechanism to certify the output.
|
| Problems and Challenges
|
A mechanism of digital signature must be provided to guarantee the authentication of the output.
|
| Additional Material
|
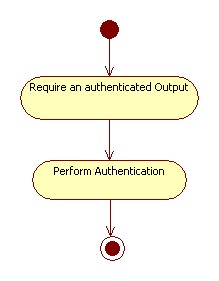
|
Table S4: Scenario TIS-ENG-4
| Field |
Description
|
| UniqueID
|
TIS-ENG-4
|
| Short Name
|
Satisfy Request
|
| Related To
|
TIS-BG-2
|
| Involved Actors
|
User, Public Body
|
| Detailed Operational Description
|
Data submitted by the user when an eGovernment service is requested, are used by the Public Body to satisfy the user requests. At the end of the process the User receives the required output.
|
| Problems and Challenges
|
A mechanism of digital signature must be provided to guarantee the authentication of the output.
|
| Additional Material
|

|







